RD 50® Radiation Shielding Glass
Monolithic X-ray protection sight-glass with increased lead equivalent
Special Properties
- Increased lead equivalent compared to RD 30®
- High X-ray absorption
- Large dimensions are possible
- More scratch-resistant than acrylic glass
- Non-flammable
- Good transparency
- A wide range of thicknesses is possible
Typical Applications
- X-ray protection glass for medical applications
- Protective windows for positron emission tomography (PET)
- Radiation protection in computed tomography (CT)
- Sight-glass for X-ray rooms
- Radiation protection doors and windows in medical radiology rooms
- Nuclear research
Related glass types
Request for Quotation
RD 50® offers increased absorption of radiation
RD 50® is a clear, transparent, dense flint glass produced by SCHOTT in Germany. The modified lead-silicate glass can shield X-rays and gamma radiation in medical, industrial, and research applications. It has a lead oxide content of > 65% by weight, which results in a density of at least 5.05 g/cm2 and thus enables compliance with statutory safety regulations even at comparatively low glass thicknesses. RD 50® has a higher lead equivalent than RD 30® and therefore offers an increased radiation shielding effect and safety (see table). The X-ray absorption of RD 50® can meet the requirements of the German Institute for Standardization (DIN Germany), European Standardization, and the International Electrotechnical Commission. RD 50® radiation shielding glass's particular composition allows for positron emission tomography (PET) and computer tomography (CT) applications and their combination. RD 50® is also often an adequate solution for shielding applications in nuclear research. The glass is available in a wide range of standard thicknesses. Often, we can polish it to a custom thickness, too. If you are searching for a radiation shielding glass optimized for mammography applications, please visit our RD 30® website.
To request a quote for sight glass or windows made of original SCHOTT RD 50® high-quality radiation shielding glass, please select a thickness from the table in the specifications or click the button below.
Please follow the installation, cleaning, and care instructions for radiation shielding glass.
Specifications
Transmission of RD50®
radiation shielding glass 5 mm thick
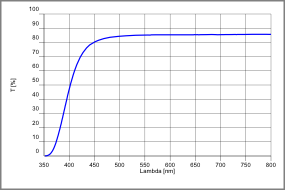
Transmission details at 5 mm thickness
Transmission of RD50®
radiation shielding glass, 20 mm thick
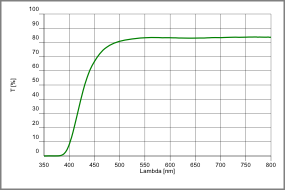
Transmission details at 20 mm thickness
Standard Thicknesses
Please click on a glass thickness to request a quote.Thickness (mm) |
Tolerance |
|---|---|
| 6.0 | ±1.0 |
| 8.0 | ±1.0 |
| 9.5 | ±1.0 |
| 11.0 | ±1.0 |
| 12.75 | ±1.25 |
| 17.5 | ±1.5 |
| 21.5 | ±1.5 |
| Custom thicknesses on request | |
Lead equivalents
| Min. thickness (mm) | 5.00 | 7.00 | 8.50 | 10.0 | 11.5 | 16.0 | 20.0 |
| Tube voltage | Lead equivalent in mm Pb | ||||||
| 76 kV* | 1.5 | 2.1 | 2.6 | 3.0 | 3.4 | -- | -- |
| 80 kV | 1.5 | 2.1 | 2.6 | 3.1 | 3.5 | -- | -- |
| 100 kV | 1.5 | 2.1 | 2.6 | 3.1 | 3.6 | 5.0 | 6.3 |
| 110 kV | 1.5 | 2.1 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 3.5 | 4.9 | 6.1 |
| 150 kV | 1.5 | 2.1 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 3.5 | 4.9 | 6.1 |
| 200 kV | 1.4 | 2.0 | 2.4 | 2.9 | 3.3 | 4.6 | 5.8 |
| 250 kV | 1.4 | 2.0 | 2.4 | 2.8 | 3.3 | 4.7 | 5.9 |
| 300 kV | 1.4 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 2.9 | 3.4 | 4.8 | 6.1 |
| 350 kV* | 1.4 | 2.1 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 3.5 | 4.9 | 6.2 |
| 400 kV | 1.5 | 2.1 | 2.6 | 3.1 | 3.6 | 5.0 | 6.4 |
| 450 kV* | 1.5 | 2.1 | 2.6 | 3.1 | 3.6 | 5.1 | 6.5 |
| 500 kV* | 1.5 | 2.2 | 2.7 | 3.2 | 3.7 | 5.2 | 6.6 |
| 550 kV* | 1.5 | 2.2 | 2.7 | 3.2 | 3.7 | 5.3 | 6.7 |
| 600 kV* | 1.6 | 2.2 | 2.7 | 3.3 | 3.8 | 5.4 | 6.8 |
| 650 kV* | 1.6 | 2.2 | 2.8 | 3.3 | 3.8 | 5.4 | 6.9 |
| 750 kV* | 1.6 | 2.3 | 2.8 | 3.4 | 3.9 | 5.5 | 7.0 |
| 1000 kV* | 1.6 | 2.4 | 2.9 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 5.7 | 7.3 |
| *no tube voltage according to DIN EN 61331-1 | |||||||
Refractive Index
- nD = 1.79
Mechanical Properties
- Density: ≥ 5.05 g/cm3
- Young's modulus E: 56.6 kN/mm2
- Poisson number µ: 0.245
- Torsion modulus G: 22.7 kN/mm2
- Knoop hardness HK 0.1/20: 360
- Stress optical coefficient C
in 1.02 × 10-12 m2/N: 0.78
Thermal Properties
- Mean linear coefficient of thermal expansion:
7.4 × 10-6/K (20 °C ; 300 °C) (static measurement) - Transformation Temperature Tg: 467 °C
- Viscosities and corresponding temperatures:
- Strain point (1014.5 dPa): 444 °C
- Annealing point (1013 dPa): 467 °C
- Softening point (107.6 dPa): 603 °C
- Forming temperature (106 dPa): 673 °C
- Forming temperature (105 dPa): 729 °C
- Forming temperature (104 dPa): 800 °C
- Mean specific heat capacity cp:
0.39 J/(g × K) (20–100 °C) - Thermal conductivity: 0.62 W/(m × K) (at 50 °C)
Chemical Properties
- Hydrolytic resistance according to DIN ISO 719:
- Hydrolytic Class HGB 1
- Equivalent of alkali (Na2O) per g of glass grains: 24 μg/g
- Acid resistance according to DIN 12 116:
- no data available
- Alkali resistance according to DIN ISO 695:
- Alkali Class A3
- Surface weight loss after 3h:
510 mg/dm2
Please make sure to observe the installation, cleaning, and maintenance instructions for radiation shielding glass.
© 1994 – 2025 Präzisions Glas & Optik GmbH
Last update: March 19, 2025


